Sparse disk image formats such as qcow2 only consume the physical disk space which they need. For example, if a guest is given a qcow2 image with a size of 100GB but has only written to 10GB then only 10GB of physical disk space will be used. There is some slight overhead associated, so the above example may not be strictly true, but you get the idea.
Sparse disk image formats such as qcow2 only consume the physical disk space which they need. For example, if a guest is given a qcow2 image with a size of 100GB but has only written to 10GB then only 10GB of physical disk space will be used. There is some slight overhead associated, so the above example may not be strictly true, but you get the idea.
Sparse disk image files allow you to over allocate virtual disk space – this means that you could allocate 5 virtual machines 100GB of disk space, even if you only have 300GB of physical disk space. If all the guests need 100% of their 100GB disk space then you will have a problem. If you use over allocation of disk space you will need to monitor the physical disk usage very carefully.
There is another problem with sparse disk formats, they don’t automatically shrink. Let’s say you fill 100GB of a sparse disk (we know this will roughly consume 100GB of physical disk space) and then delete some files so that you are only using 50GB. The physical disk space used should be 50GB, right? Wrong. Because the disk image doesn’t shrink, it will always be 100GB on the file system even if the guest is now using less. The below steps will detail how to get round this issue.
On Linux
We need to fill the disk of the guest with zero’s (or any other character) so that the disk image can be re-compressed.
In a terminal, run the below command until you run out of disk space. Before running this, be sure to stop any applications running on the guest otherwise errors may result.
dd if=/dev/zero of=/mytempfile
Once the command errors out (this may take a while depending on your disk image size and physical disk speed) delete the file.
rm -f /mytempfile
Shutdown the guest and follow the steps below under All OS’s.
On Windows
You will need to download a tool called sdelete from Microsoft which is will fill the entire disk with zeros which can be re-compressed later.
Download: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/sysinternals/bb897443.aspx
Once you have downloaded and extracted sdelete, open up a command prompt and enter the following. This assumes that sdelete was extracted into c:\ and c:\ is the disk you would like to use to reclaim space
c:\sdelete.exe -z c:
Once this completes (this may take a while depending on your disk image size and physical disk speed), shutdown the guest and follow the below steps under All OS’s.
All OS’s
The rest of the process is done on the host so open up a terminal window and SSH to your Proxmox host. Move to the directory where the disk image is stored and run the below commands.
Make sure you have shut down the virtual machine which is using the qcow2 image file before running the below commands.
mv original_image.qcow2 original_image.qcow2_backup
qemu-img convert -O qcow2 original_image.qcow2_backup original_image.qcow2
The above commands move the original image file, and then re-compress it to it’s original name. This will shrink the qcow2 image to consume less physical disk space.
You can now start the guest and check that everything is in working order. If it is, you can remove the original_image.qcow2_backup file.
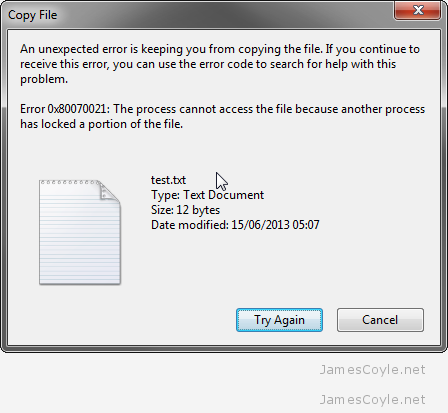 I had a problem with a SMB share which was sharing storage from an NFS mount.
I had a problem with a SMB share which was sharing storage from an NFS mount.